Technology
Functions of Stamping Press
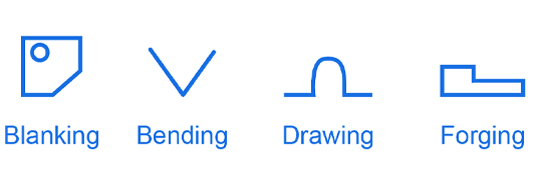
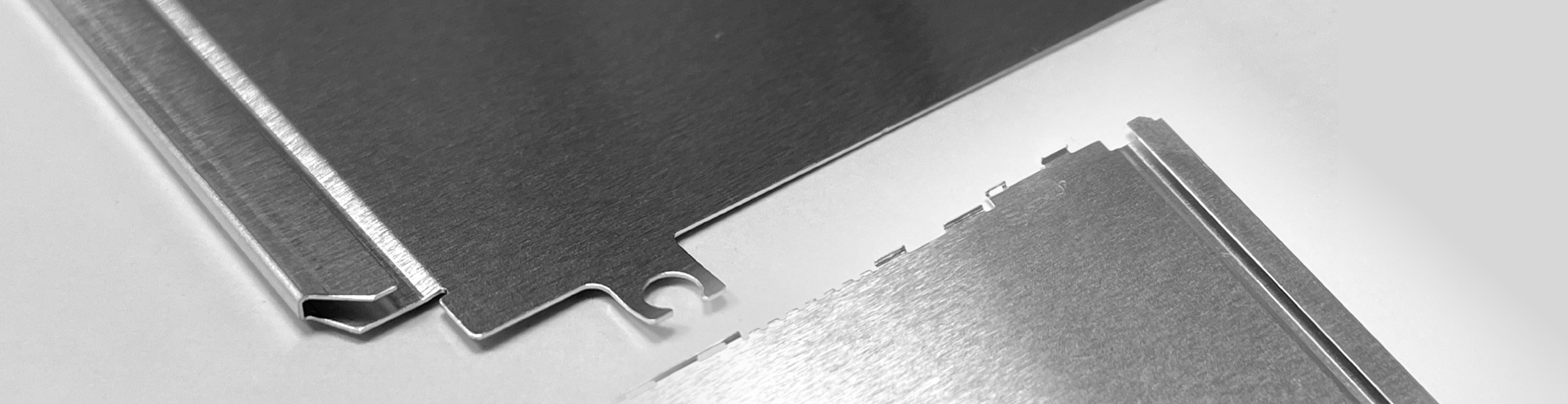
A stamping press is a versati le metal sheet processing equipment used for tasks such as blanking, punching, forming, deep drawing, trimming, fi ne punching, shaping, riveting, and extruding when paired with with dies or tools. It finds widespread applicati on across diverse industries. Everyday items such as switches, beverage cans, batteries, and aircraft components rely heavily on punch presses and molds for producti on.
What is High-Speed Stamping Press?
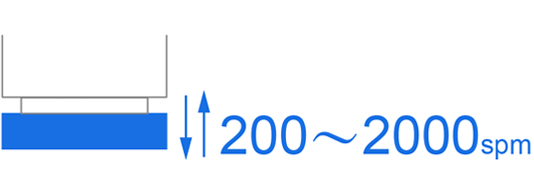
Discover the effi ciency and precision of a high-speed stamping press, a specialized metal forming machine engineered for rapid producti on of high-volume, smaller components. Known for delivering products with excepti onal precision, superior surface quality, and extended die longevity, these presses are indispensable in industries including 3C (communicati ons, computers, consumer electronics), household appliances, automoti ve parts, and motor stators and rotors.
What is Manual Scraping?
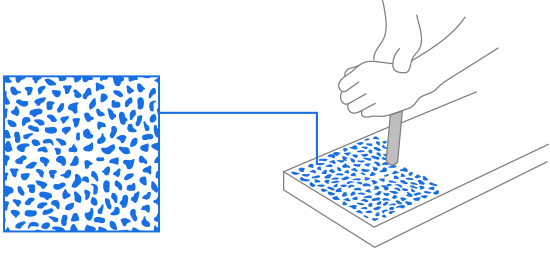
During machine assembly, many metal surfaces need to fit together seamlessly. However, even finely ground surfaces cannot achieve perfect consistency when placed together. Therefore, it is necessary to achieve a tighter fit of the machine base through scraping to achieve higher assembly accuracy and maintain long-term stability during the stamping operation.
How to Choose Stamping Press?

Stamping presses come in various types, categorized by their body form as C frame (C type) and straight column type (H type). They are further classified based on the driving force: mechanical presses, pneumatic presses, or hydraulic presses. But how does one select the right stamping press?
Three critical factors should guide your decision:
Three critical factors should guide your decision:
- Raw Material Properties: Consider the type, thickness, and hardness of the raw material.
- Production Volume and Capacity: Evaluate the quantity and production capacity requirements.
- Product Specifications and Precision Needs: Assess the specific specifications and accuracy requirements of the products.

